An old king wants to divide his kingdom between his two sons. He is well known for his justness and wisdom, and he plans to make a good use of both of these attributes while dividing his kingdom.
The kingdom is administratively split into square boroughs that form an N × M grid. Some of the boroughs contain gold mines. The king knows that his sons do not care as much about the land as they do about gold, so he wants both parts of the kingdom to contain exactly the same number of mines. Moreover, he wants to split the kingdom with either a horizontal or a vertical line that goes along the borders of the boroughs (splitting no borough into two parts).
The goal is to count how many ways he can split the kingdom.
Write a function:
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y);
that, given two arrays of K integers X and Y, denoting coordinates of boroughs containing the gold mines, will compute the number of fair divisions of the kingdom.
For example, given N = 5, M = 5, X = [0, 4, 2, 0] and Y = [0, 0, 1, 4], the function should return 3. The king can divide his land in three different ways shown on the picture below.
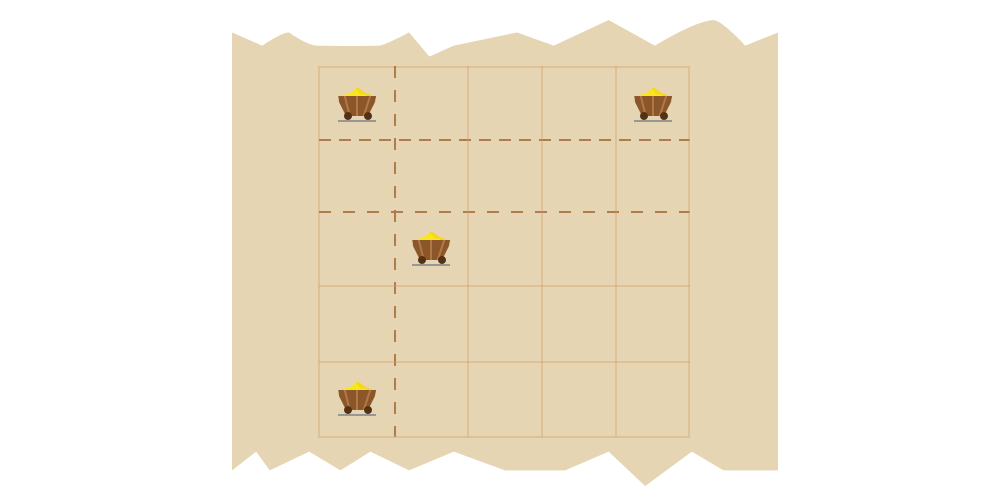
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N and M are integers within the range [1..100,000];
- K is an integer within the range [1..100,000];
- each element of array X is an integer within the range [0..N-1];
- each element of array Y is an integer within the range [0..M-1].
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// write your code in C++14 (g++ 6.2.0)
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
//
if (K % 2)
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this
if (K % 2)
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << f
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << flush;
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", ""
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcount[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
}func.cpp: In function 'int solution(int, int, std::vector<int>&, std::vector<int>&)':
func.cpp:28:9: error: 'colcount' was not declared in this scope
colcount[Y[i]]++;
^~~~~~~~
func.cpp:39:1: warning: control reaches end of non-void function [-Wreturn-type]
}
^
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
co
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
vector<int> colcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if 8
}
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
ways =
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return 0;
}2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
ways ++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1,
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 3
1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 1, 3, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 1, 3, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
for (int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
}
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
for (int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i])
}
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways +=
for (unsigned int i=0;i<rowcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
rowcounts[i] += rowcounts[i-1];
if (rowcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (rowcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0;i<colcounts.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
colcounts[i] += colcounts[i-1];
if (colcounts[i] > divisor)
break;
if (colcounts[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
for (int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 1, 3, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
if (i > 0)
sum[i]+= sum[i-1];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (sum[i] > divisor)
break;
if (sum[i] == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(cvector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}func.cpp: In function 'int calculateCounts(const std::vector<int>&, int)':
func.cpp:16:12: error: expected '(' before 'currentSum'
if currentSum > divisor)
^~~~~~~~~~
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
#inc
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}// you can use includes, for example:
// #include <algorithm>
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexit
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
//
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// still inside
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line to
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}function result: 1
function result: 4
function result: 1
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 1, [0, 0], [4, 0]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 1, [0, 0], [4, 0]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 1, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}function result: 1
function result: 4
function result: 4
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1,
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cout << rowcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
cout << endl << endl;
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
cout << colcounts[i] << ", " << flush;
}
return ways;
}2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 1
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
function result: 4
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1,
function result: 0
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]
[8, 8, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}function result: 1
function result: 4
function result: 4
function result: 0
function result: 2
function result: 2
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]
[8, 8, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
/**
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
*
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in]
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] sum
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &sum,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] sum
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += sum[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair di
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/**
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** Ho
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** How many ways can the King split the kingdom.
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Assumes X and Y size
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Assumes X and Y must be pairs.
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Finds and calculates a fair dividing Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only beAssumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines given with X and Y variables.Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines given with X and Y variable.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* @param[in] N
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* @param[in] N Row count of a
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in]
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* -
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}func.cpp: In function 'int calculateCounts(const std::vector<int>&, int)':
func.cpp:19:29: error: 'sum' was not declared in this scope
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
^~~
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}func.cpp: In function 'int calculateCounts(const std::vector<int>&, int)':
func.cpp:19:29: error: 'sum' was not declared in this scope
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sum.size();i++)
^~~
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<counts.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<counts.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}function result: 1
function result: 4
function result: 4
function result: 0
function result: 2
function result: 2
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]
[8, 8, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<counts.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}function result: 1
function result: 4
function result: 4
function result: 0
function result: 2
function result: 2
[5, 5, [1, 4, 2, 0], [1, 0, 1, 4]]
[1, 5, [0, 0], [0, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 3, 4], [0, 1, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]
[8, 8, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
[5, 5, [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/**
* Calculate Counts of a Row or Column
* Calculates sums until given index on a row or a column and returns number of ways to divide on that set of rows or columns.
*
* @param[in] counts row/columns gold mine counts
* @param[in] divisor fair division line
* @return number of ways division possible using this set
*/
int calculateCounts(const vector<int> &counts,int divisor)
{
int ways = 0;
int currentSum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<counts.size();i++)
{
currentSum += counts[i];
// Moved to an unfair line ? just break this loop
if (currentSum > divisor)
break;
// if still in a fair line than we could count this line as a way to divide the kingdom.
if (currentSum == divisor)
ways++;
}
return ways;
}
/** This function calculates how many ways can the King split the kingdom for his two children.
* Finds ways to divide a kindgom for the king.
* - Kingdom can only be split using vertical and horizontal lines goes along the borders.
* - Each divided part must contain same amount of gold mines.
* - Assumes X and Y must be pairs and no duplicates.
* - Assumes gold mines can't be shared.
* - Assumes only gold mines matter; land does not.
* @param[in] N Row count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] M Column count of the Kingdom
* @param[in] X X coordinates of the goldmines.
* @param[in] Y Y coordinates of the goldmines.
* @return Number of ways that goldmines can be split equally between two childrens.
*/
int solution(int N, int M, vector<int> &X, vector<int> &Y) {
// Just some sanity checks
// cordinates must be pairs.
if (X.size() != Y.size())
return 0;
int K = X.size();
// Gold mines must be divisable by two if we want this to be fair.
if (K % 2)
return 0;
// Count number of gold mines in a row and in a column
vector<int> rowcounts(N,0);
vector<int> colcounts(M,0);
// If we sort the X/Y coordinate pairs before this loop; solution can be realized inside this single for loop. I didn't implement this solution just because it might break max allowed time complexity.
for (int i=0;i<K;i++)
{
if (X[i] < N) // Check if coordinate is inside the kingdom
rowcounts[X[i]]++;
if (Y[i] < M)
colcounts[Y[i]]++;
}
int ways = 0;
int divisor = K / 2;
ways = calculateCounts(rowcounts,divisor);
ways += calculateCounts(colcounts,divisor);
return ways;
}The solution obtained perfect score.