We draw N discs on a plane. The discs are numbered from 0 to N − 1. An array A of N non-negative integers, specifying the radiuses of the discs, is given. The J-th disc is drawn with its center at (J, 0) and radius A[J].
We say that the J-th disc and K-th disc intersect if J ≠ K and the J-th and K-th discs have at least one common point (assuming that the discs contain their borders).
The figure below shows discs drawn for N = 6 and A as follows:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 5 A[2] = 2 A[3] = 1 A[4] = 4 A[5] = 0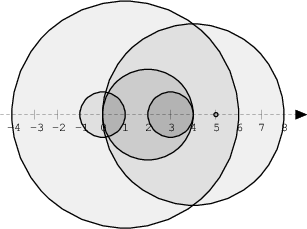
There are eleven (unordered) pairs of discs that intersect, namely:
- discs 1 and 4 intersect, and both intersect with all the other discs;
- disc 2 also intersects with discs 0 and 3.
Write a function:
function solution(A);
that, given an array A describing N discs as explained above, returns the number of (unordered) pairs of intersecting discs. The function should return −1 if the number of intersecting pairs exceeds 10,000,000.
Given array A shown above, the function should return 11, as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N is an integer within the range [0..100,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..2,147,483,647].
 The submission is being evaluated.
The submission is being evaluated.