A country network consisting of N cities and N − 1 roads connecting them is given. Cities are labeled with distinct integers within the range [0..(N − 1)]. Roads connect cities in such a way that each distinct pair of cities is connected either by a direct road or through a path consisting of direct roads. There is exactly one way to reach any city from any other city.
Starting out from city K, you have to plan a series of daily trips. Each day you want to visit a previously unvisited city in such a way that, on a route to that city, you will also pass through a maximal number of other unvisited cities (which will then be considered to have been visited). We say that the destination city is our daily travel target.
In the case of a tie, you should choose the city with the minimal label. The trips cease when every city has been visited at least once.
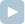
For example, consider K = 2 and the following network consisting of seven cities and six roads:

You start in city 2. From here you make the following trips:
- day 1 − from city 2 to city 0 (cities 1 and 0 become visited),
- day 2 − from city 0 to city 6 (cities 4 and 6 become visited),
- day 3 − from city 6 to city 3 (city 3 becomes visited),
- day 4 − from city 3 to city 5 (city 5 becomes visited).
The goal is to find the sequence of travel targets. In the above example we have the following travel targets: (2, 0, 6, 3, 5).
Write a function:
class Solution { public int[] solution(int K, int[] T); }
that, given a non-empty array T consisting of N integers describing a network of N cities and N − 1 roads, returns the sequence of travel targets.
Array T describes a network of cities as follows:
- if T[P] = Q and P ≠ Q, then there is a direct road between cities P and Q.
For example, given the following array T consisting of seven elements (this array describes the network shown above) and K = 2:
T[0] = 1 T[1] = 2 T[2] = 3 T[3] = 3 T[4] = 2 T[5] = 1 T[6] = 4the function should return a sequence [2, 0, 6, 3, 5], as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N is an integer within the range [1..90,000];
- each element of array T is an integer within the range [0..(N−1)];
- there is exactly one (possibly indirect) connection between any two distinct roads.