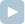
There is an N × N square mesh-shaped grid of wires, as shown in a figure below. Nodes of the grid are at points (X, Y), where X and Y are integers from 0 to N−1. An electric current flows through the grid, between the nodes at (0, 0) and (N−1, N−1).

Initially, all the wires conduct the current, but the wires burn out at a rate of one per second. The burnouts are described by three arrays of integers, A, B and C, each of size M. For each moment T (0 ≤ T < M), in the T-th second the wire between nodes (A[T], B[T]) and:
- (A[T], B[T] + 1), if C[T] = 0 or
- (A[T] + 1, B[T]), if C[T] = 1
burns out. You can assume that the arrays describe existing wires, and that no wire burns out more than once. Your task is to determine when the current stops flowing between the nodes at (0,0) and (N−1,N−1).
Write a function:
class Solution { public int solution(int N, int[] A, int[] B, int[] C); }
that, given integer N and arrays A, B and C, returns the number of seconds after which the current stops flowing between the nodes at (0, 0) and (N−1, N−1). If the current keeps flowing even after all M wires burn out, the function should return −1.
For example, given N = 4, M = 9 and the following arrays:
A[0] = 0 B [0] = 0 C[0] = 0 A[1] = 1 B [1] = 1 C[1] = 1 A[2] = 1 B [2] = 1 C[2] = 0 A[3] = 2 B [3] = 1 C[3] = 0 A[4] = 3 B [4] = 2 C[4] = 0 A[5] = 2 B [5] = 2 C[5] = 1 A[6] = 1 B [6] = 3 C[6] = 1 A[7] = 0 B [7] = 1 C[7] = 0 A[8] = 0 B [8] = 0 C[8] = 1your function should return 8, because just after the eighth wire burns out, there is no connection between the nodes at (0, 0) and (N−1, N−1). This situation is shown in the following figure:

Given N = 4, M = 1 and the following arrays:
A[0] = 0 B [0] = 0 C[0] = 0your function should return −1, because burning out a single wire cannot break the connection between the nodes at (0, 0) and (N−1, N−1).
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N is an integer within the range [1..400];
- M is an integer within the range [0..2*N*(N-1)];
- each element of arrays A and B is an integer within the range [0..N-1];
- each element of array C is an integer that can have one of the following values: 0, 1.